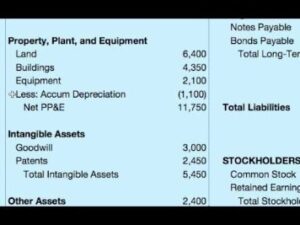
The figure below is an example of how Equity is reported on the Balance Sheet of a corporation when stock has been issued. Stockholders’ equity is also the corporation’s total book value (which is different from the corporation’s worth or market value). PwC refers to the US member firm or one of its subsidiaries or affiliates, and may sometimes refer to the PwC network.
- This statement is important because it shows how the company’s net worth has changed over time.
- If the company ever needs to be liquidated, SE is the amount of money that would be returned to these owners after all other debts are satisfied.
- Statement of Shareholders’ Equity is a financial statement that shows the changes in a company’s equity over a period of time.
- Long-term assets are assets that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year.
- A debt issue doesn’t affect the paid-in capital or shareholders’ equity accounts.
Retained earnings are part of shareholder equity and are the percentage of net earnings not paid to shareholders as dividends. Retained earnings should not be confused with cash or other liquid assets. This is because years of retained earnings could be used for either expenses or any asset type to grow the business. Keep in mind that shareholder equity, though, is not the same as liquidation value. In liquidation, physical asset values are reduced and other extraordinary conditions exist.
It can tell you how well you’re running your business.
Calculating stockholders equity is an important step in financial modeling. This is usually one of the last steps in forecasting the balance sheet Reporting Stockholder Equity items. Below is an example screenshot of a financial model where you can see the shareholders equity line completed on the balance sheet.

It can also help you attract outside investors who will undoubtedly want to see that statement prior to injecting capital into your enterprise. A dividend is the amount of money paid per share of stock, and it is not necessarily equal to the profit. Instead, the company will set aside a portion of its profits to pay dividends, and that portion is usually outlined in the stock agreement. When you take all of the company’s assets and subtract the liabilities, what remains is the equity. For a company with stock shares, the equity is owned by the stockholders. The statement of equity is simply the part of a balance sheet or ledger that clearly calculates and explains the stockholders’ (or shareholders’) equity.
What is stockholders’ equity?
Finding it on the balance sheet is one way you can learn about the financial health of a firm. Stockholders’ equity and liabilities are also seen as the claims to the corporation’s assets. However, the stockholders’ claim comes after the liabilities have been paid. A company’s shareholders’ equity is fluid, often changing several times during a year due to actions taken by the company, which can affect one or more of the components. However, shareholders’ equity alone may not provide a complete assessment of a company’s financial health. Stockholders’ equity is a line item that can be found on a company’s balance sheet, and the trend in stockholders’ equity can be assessed by looking at past balance sheet reports.
What is stockholder equity on the balance sheet?
Stockholders' equity is the amount of assets remaining in a business after all liabilities have been settled. It is calculated as the capital given to a business by its shareholders, plus donated capital and earnings generated by the operation of the business, less any dividends issued.
The retained earnings portion reflects the percentage of net earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends and should not be confused with cash or other liquid assets. Shareholder equity helps determine the return being generated versus the total amount invested by equity investors. Positive shareholder equity means the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities but if it is negative, the company’s liabilities exceed its assets. This is cause for concern because it tells you the value of a business after investors and stockholders are paid out. Share Capital (contributed capital) refers to amounts received by the reporting company from transactions with shareholders. Common shares represent residual ownership in a company and in the event of liquidation or dividend payments, common shares can only receive payments after preferred shareholders have been paid first.
Return on Assets
It should be noted that the value of common and preferred shares is recorded at par value on the balance sheet, so the amount shown doesn’t necessarily equal or approximate the company’s market value. When a company buys shares from its shareholders and doesn’t retire them, it holds them as treasury shares in a treasury stock account, which is subtracted from its total equity. For example, if a company buys back 100,000 shares of its common stock for $50 each, it reduces stockholders’ equity by $5,000,000. For many companies, paid-in capital is a primary source of stockholders’ equity. Paid-in capital is the money companies bring in by issuing stock to the public.
Where is stockholders equity reported?
Stockholders' equity is equal to a firm's total assets minus its total liabilities. These figures can all be found on a company's balance sheet.
The value of $65.339 billion in shareholders’ equity represents the amount left for stockholders if Apple liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its liabilities. To calculate retained earnings, the beginning retained earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted. A summary report called a statement of retained earnings is also maintained, outlining the changes in retained earnings for a specific period. Stockholders Equity provides highly useful information when analyzing financial statements.
What is stockholders’ equity?
If it’s positive, the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities. If a company’s shareholder equity remains negative, it is considered to be balance sheet insolvency. Current assets can be converted to cash within a year, such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory among others. Long-term assets are assets that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year. These assets include investments; property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangibles like patents.
- A statement of stockholders’ equity is another name for the statement of shareholder equity.
- A company’s total number of outstanding shares of common stock, including restricted shares, issued to the public, company officers, and insiders is a key driver of stockholders’ equity.
- Stockholders’ equity and liabilities are also seen as the claims to the corporation’s assets.
- Companies have no obligation whatsoever to pay out dividends until they have been formally declared by the board.
If that happens, it increases stockholders’ equity by the par value of the issued stock. For example, if a company issues 100,000 common shares for $40 each, the paid-in capital would be equal to $4,000,000 and added to stockholders’ equity. A company’s total number of outstanding shares of common stock, including restricted shares, issued to the public, company officers, and insiders is a key driver of stockholders’ equity. The amount recorded is based on the par value of the common and preferred stock sold by the company not the current market value.
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods longer than one year. Companies may have bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations under this category. Retained earnings (RE) are a company’s net income from operations and other business activities retained https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/federal-income-tax-calculator/ by the company as additional equity capital. They represent returns on total stockholders’ equity reinvested back into the company. Equity, also referred to as stockholders’ or shareholders’ equity, is the corporation’s owners’ residual claim on assets after debts have been paid.
Once you have viewed this piece of content, to ensure you can access the content most relevant to you, please confirm your territory. These materials were downloaded from PwC’s Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license. Stockholders’ equity has a few components, each with its own value and meaning. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.